
WLTP standard - definition
Worldwide harmonized Light vehicule Test Procedure
The WLTP standard is a worldwide protocol for determining the CO2 pollution levels of internal combustion vehicles. The standard was introduced by the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe ( UNECE ) in 1990.
The WLTP standard has replaced the NEDC ( New European Driving Cycle) since September 2017.
What is it used for? It is used to measure the fuel consumption and CO2 emissions of vehicles on the road, under more precise, real-life conditions.
- It will harmonize standards between countries
- Replace obsolete test conditions
- Reinforcing test safety - Dieselgate scandal
- Meeting international climate targets
Who is it for? It applies to car users, and dealers since September 1, 2017 in the European Union. The WLTP standard replaces the NEDC standard, which had previously applied since 1992.
In which countries does it apply?
- The 28 steps of the European Community
- In Norway, Iceland, Switzerland, Turkey and Israel
Where and how are the tests carried out?
Tests for the WLTP cycle are carried out in the laboratory on roller benches. These tests take into account as many situations as possible that motorists may encounter. These include weather conditions, terrain, vehicle load, driving style, road types, etc. The options offered by electric vehicle models are also taken into account, since they have a significant impact on weight and fuel consumption.
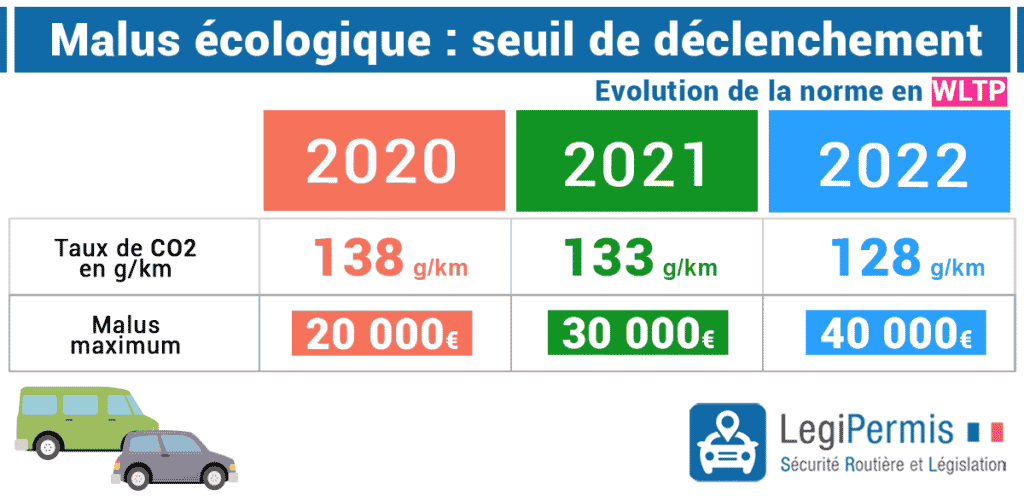
Table: Ecological penalty (wltp)
Similar articles:
- WLTP standard: definition and changes for motorists and corporate fleets
- Ecological surcharge: a new increase planned for 2023
- CAFE regulations: One more reason to go electric
Do you have any further questions?
"All definitions